Your cart is currently empty!

Explanation of CyberSecurity as a Service (CSaaS) 2024
Table of Contents
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, organizations face the challenge of safeguarding their digital assets. Cybersecurity as a Service (CSaaS) emerges as a strategic solution, offering comprehensive cybersecurity management through third-party expertise. This model, adaptable and cost-effective, is gaining traction across various business sectors.
Understanding Cybersecurity as a Service (CSaaS) Model
CSaaS is an innovative approach where businesses outsource their cybersecurity needs to specialized vendors. These services typically include:
- Initial cybersecurity consultations
- Security essentials evaluations
- Employee training in cybersecurity awareness
- Regular penetration testing
- Continual anti-virus updates
- Compliance with legal and industry standards
- Business continuity planning
The Evolution and Significance of CSaaS
The rapidly evolving cybercrime landscape necessitates robust defence mechanisms. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), often lacking in-house cybersecurity expertise, are increasingly adopting CSaaS. A recent survey revealed that 62% of organizations are implementing CSaaS because of its flexibility and comprehensive coverage.

Key Advantages of CSaaS
- Cost-Effectiveness: CSaaS mitigates the high costs associated with building and maintaining an in-house cybersecurity team, offering a financially viable solution for businesses, especially those with limited IT budgets.
- Expertise on Demand: Access to cybersecurity specialists provides businesses with advanced and tailored defense strategies. This expertise is vital for SMBs, who are frequent targets of cyber attacks.
- Reduced HR Strain: The growing demand for cybersecurity professionals has created a talent shortage. CSaaS alleviates the burden on HR departments by providing round-the-clock expert availability.
- Scalability: CSaaS offers flexibility, allowing businesses to adjust their cybersecurity measures in line with their evolving needs and growth trajectories.
- Focus on Core Business Operations: By outsourcing cybersecurity, businesses can concentrate on their primary operations, enhancing productivity and customer experiences.
Choosing the Right CSaaS Provider: Key Considerations
Selecting a suitable CSaaS provider requires thorough evaluation based on:
- Provider’s experience and industry reputation
- Alignment with the company’s size and sector
- Services offered and their customizability
- Economic feasibility and cost structure
- Proven track record and references from credible sources.
Prioritizing Cybersecurity with CSaaS
In a world where cybersecurity is a critical investment, CSaaS presents a strategic, flexible, and cost-effective solution. It enables businesses to navigate the complexities of digital threats while focusing on their core competencies. With its growing popularity, CSaaS stands as a pivotal tool for modern businesses to ensure robust cybersecurity.
Diagram: The CSaaS Model – An Overview
This flowchart depicts the interaction between businesses and CSaaS providers, highlighting the dynamic exchange of needs, solutions, and benefits, culminating in enhanced security and operational focus.
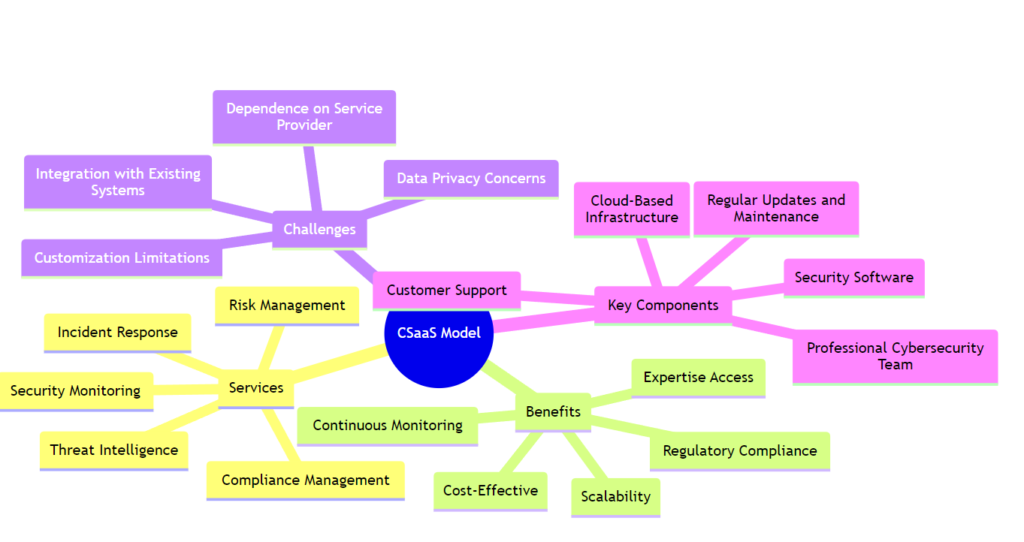
The Essence of CSaaS
CSaaS Defined: At its core, CSaaS is a subscription-based model that provides businesses with a range of cybersecurity services. This model includes threat intelligence, monitoring, incident response, and more, delivered through the cloud.
Advantages of CSaaS:
- Scalability: Easily adaptable to the changing needs of businesses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for in-house cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Expertise: Access to top-tier security experts and technologies.
Key Components of CSaaS
- Threat Intelligence and Monitoring: Continuous surveillance for potential threats, ensuring proactive defense.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Regular evaluations of potential risks and implementation of strategies to mitigate them.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Rapid response to security incidents, minimising damage and restoring normal operations.
- Compliance and Governance: Ensuring adherence to relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards.
Implementing CSaaS in Your Business
Implementing CSaaS requires a strategic approach:
- Assessment of Needs: Understanding specific security requirements.
- Choosing the Right Provider: Selecting a CSaaS provider that aligns with your business objectives and security needs.
- Integration and Deployment: Seamlessly integrating CSaaS solutions with existing IT infrastructure.
- Ongoing Management and Evolution: Regularly reviewing and updating cybersecurity strategies to combat emerging threats.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Embracing CSaaS
The evolution of cyber threats demands a dynamic and robust approach to security. CSaaS represents the future of cybersecurity, offering businesses a way to stay ahead of threats while optimizing resources.
What is CSA in cybersecurity?
The premier global organisation for developing and disseminating best practises to support the maintenance of a secure cloud computing environment is the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA).
What value does cybersecurity as a service provide organizations?
Cybersecurity services can help businesses avoid costly fines or ransom payments, safeguard sensitive data, and stop cyberattacks—all of which can help them maintain their good name. One of an organization’s most valuable assets is its reputation, which can take years to rebuild after a data breach.
What are the 5 security services in cyber security?
Define data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, non-repudiation, and access control as the five security services that guard against security breaches. steganography, cryptography, and demonstrate how symmetric-key or asymmetric-key cyphers can be used to provide secrecy.
What is an example of security as a service?
SECaaS services include, for instance: Data loss prevention (DLP) ongoing observation. Recovery from disasters.
What are cybercrime tools?
Tools for digital forensics may include programmes such as Autopsy, FTK, and EnCase. Cybercrime investigators may employ a variety of additional methods in addition to digital forensics in order to obtain information and identify potential suspects.

Leave a Reply